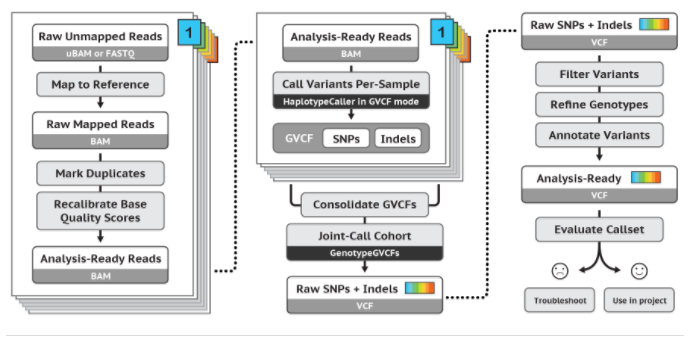
GATK4推荐流程。 其实还没完全搞懂。 不过把变异call出来是没问题的! 没有和其他软件对比过正确率。。。
#1 首先把原始数据处理成可以用 的bam 参考推荐的数据准备流程。
#2 同样的,配置好软件和环境 像这样。
sample=sample.pre.analysis.bam
gatk=/software/gatk-4.0.0.0/gatk
reference=/database/GATK/hg19/ucsc.hg19.fasta
omni=/database/GATK/hg19/1000G_omni2.5.hg19.vcf
indel=/database/GATK/hg19/1000G_phase1.indels.hg19.vcf
dbsnp=/database/GATK/hg19/dbsnp_138.hg19.vcf
hapmap=/database/GATK/hg19/hapmap_3.3.hg19.vcf
snp=/database/GATK/hg19/1000G_phase1.snps.high_confidence.hg19.vcf
#3 生成gvcf haplotypecaller运行每个样本以生成称为gvcf的中间文件,然后可以以非常有效的方式用于多个样本的联合基因分型。
$gatk --java-options "-Xmx4g" HaplotypeCaller \
-R $reference \
-I $sample \
-O output.g.vcf.gz \
-ERC GVCF
#4 生成vcf 收集所有的每个样本gvcfs(或者如果处理大量的样本,合并gvcfs),然后将它们传递给联合基因分型工具genotypegvcfs。 这产生了一组联合的snp和indel,用于过滤。
$gatk --java-options "-Xmx4g" GenotypeGVCFs \
-R $reference \
-V output.g.vcf.gz \
-O output.vcf.gz
#addition 生成一个clean vcf(其实这一步不是gatk4的推荐步骤,是一个选择) 做这一步的话后面的就不用做了。不做这一步的话就做后面的。
$gatk SelectVariants \
-R $reference \
-V output.vcf.gz \
--select-type-to-include SNP \
-O output.vcf
#5 过滤前文件的生成 这一步利用了machine learning,生成过滤文件
$gatk VariantRecalibrator \
-R $reference \
-V output.vcf.gz \
--resource hapmap,known=false,training=true,truth=true,prior=15.0:$hapmap \
--resource omni,known=false,training=true,truth=false,prior=12.0:$omni \
--resource 1000G,known=false,training=true,truth=false,prior=10.0:$snp \
--resource dbsnp,known=true,training=false,truth=false,prior=2.0:$dbsnp \
-an QD -an MQ -an MQRankSum -an ReadPosRankSum -an FS -an SOR \
-mode SNP \
-O output.recal \
--tranches-file output.tranches \
--rscript-file output.plots.R
#7 根据过滤文件过滤vcf,得到clean vcf
$gatk ApplyVQSR \
-R $reference \
-V output.vcf.gz \
-O output.clean.vcf.gz \
-ts-filter-level 99.0 \
--tranches-file output.tranches \
--recal-file output.recal \
-mode SNP
#8 vcf注释 最常用的肯定是annovar啦,以前说过的,翻翻以前的文章就懂了。