总所周知,融合基因的断点大都在内含子上,这时我们有一个基因的转录本号,比如NM_004304(ALK),需要找到18号内含子。
查找的方法有通过ensembl或者biomart包,又或者cruzdb库来找。以前做过类似的事。
不过想着既然本地已经有refFlat在了,干脆就解析refFlat好了。
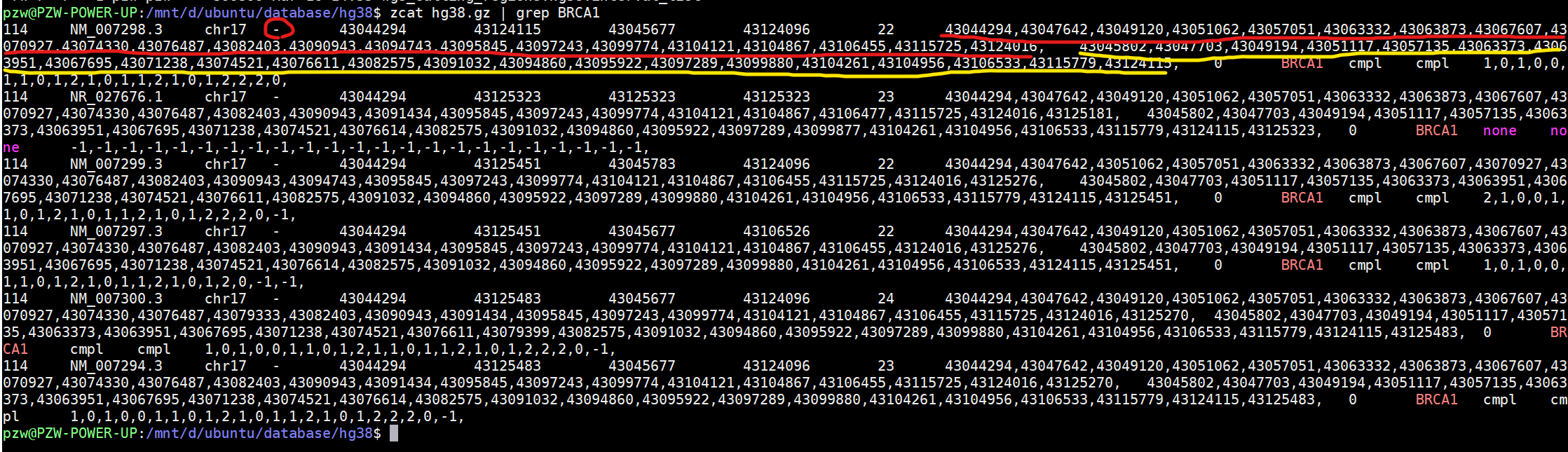
refFlat文件从左到右,每一列分别是基因名,转录本名,染色体编号,方向,转录本起始,转录本终止,cds起始,cds终止,外显子个数,各个外显子起始,各个外显子终止。
这时,简单的把上一个外显子的终止和下一个外显子的起始来当作中间夹杂的内含子的起始和终止位点。
本来想用cut管道做的,但是我不会,所以后面用python算了。
cat refFlat.txt | grep NM_004304 | cut -d$'\t' -f1,2,3,5,6
这样
db = open("refFlat.txt", "r")
refFlatIntronDict = {}
for line in db:
lines = line.split("\t")
transcript = lines[1]
refFlatIntronDict[transcript] = {}
chrom = lines[2]
strand = lines[3]
exon_start = lines[9].split(",")[:-1]
exon_end = lines[10].split(",")[:-1]
intron_start = exon_end[:-1]
intron_end = exon_start[1:]
if strand == "-":
intron_start = intron_start[::-1]
intron_end = intron_end[::-1]
n = 0
while n < len(intron_start):
refFlatIntronDict[transcript]["intron_" + str(n + 1)] = [intron_start[n], intron_end[n]]
n += 1
db.close()
把整个refFlat解析到一个字典里了。
换一种写法,可能性能会好一点,把所有exon的起始和终止坐标都解析到字典中。
db = open("refFlat.txt", "r")
refFlatDict = {}
for line in db:
refFlatExonList = []
lines = line.split("\t")
transcript = lines[1]
chrom = lines[2]
strand = lines[3]
exon_start = lines[9].split(",")[:-1]
exon_end = lines[10].split(",")[:-1]
for s in exon_start:
refFlatExonList.append(s)
for e in exon_end:
refFlatExonList.append(e)
refFlatDict[transcript] = {"strand": strand, "exonMark": refFlatExonList}
# 判断位点位置
def location(refFlatDict, transcript, queryPoint):
transDict = refFlatDict[transcript]
strand = transDict["strand"]
exonMark = transDict["exonMark"]
exonMark.append(queryPoint)
if strand == "-":
exonMark.sort(reverse=True)
else:
exonMark.sort(reverse=False)
idxQuery = exonMark.index(queryPoint)
# 索引双数时是内含子
if idxQuery % 2 == 0:
loca = "intron" + str(int(idxQuery / 2))
# 索引单数时是外显子
else:
loca = "exon" + str(int((idxQuery + 1) / 2))
return loca